Factors That Accelerate Diabetes Progression: Alcohol Consumption Ranks Only 5th - The Top Factor Is Done Daily by Many Patients
"Diabetic patients live half by controlling blood sugar, and half by preventing complications." However, some seemingly harmless habits quietly accelerate the progression of diabetes. Alcohol, sweets, and staying up late—these seemingly obvious risk factors are already being monitored by many, yet they are not the "number one culprit."

The factor that truly tops the list is often overlooked and even considered a "taken-for-granted" daily habit. This habit not only makes blood sugar control difficult but also triggers various complications, significantly reducing patients' quality of life.
Sedentary lifestyle: The invisible killer, ranking first
Sedentary behavior is a hallmark of modern lifestyles, yet its harm to diabetic patients is often underestimated. Traditional Chinese medicine emphasizes that "prolonged sitting harms qi," as prolonged inactivity can lead to poor circulation of qi and blood, impair spleen and stomach functions, and consequently promote the accumulation of dampness and turbid phlegm in the body.

Modern medicine has also found that prolonged sitting directly affects insulin sensitivity, reducing its ability to regulate blood sugar. Additionally, it increases visceral fat accumulation, exacerbating insulin resistance and leading to greater blood sugar fluctuations.

The harm of prolonged sitting extends further. It also causes a decline in muscle mass—the primary tissue responsible for glucose consumption. When muscle mass decreases, even with normal insulin secretion, glucose utilization declines, causing persistently elevated blood sugar levels. Over time, blood vessels, nerves, the heart, and other organs can be affected, significantly increasing the risk of chronic complications.

Solving prolonged sitting issues isn't difficult. The key lies in changing habits to get the body "moving." Even brief standing periods or light activity can improve blood circulation and enhance insulin efficiency. For diabetic patients, daily moderate exercise could be considered the best "medication" - it not only lowers blood sugar but also helps with weight management, improves cardiopulmonary function, and even relieves stress.
Hidden Sugars and Processed Foods: The "Stumbling Blocks" of Blood Sugar Management
Diet is at the core of diabetes management, but many patients overlook the "hidden sugars" and trans fats in food. Hidden sugars refer to invisible, tasteless sugars that are widely present in various processed foods, such as seasoning sauces, frozen foods, and ready-to-drink beverages.

Although these sugars do not directly present as sweet taste, they can be rapidly absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract, converted into glucose, and enter the bloodstream, leading to significant postprandial blood glucose fluctuations.

Trans fats are another "toxin" found in processed foods. They are often used to extend the shelf life of food products but pose significant risks to human health. Trans fats interfere with fat metabolism, increase insulin resistance, and contribute to the development of cardiovascular diseases.

For diabetic patients, consuming trans fats is like adding fuel to the fire—not only increasing the burden on pancreatic islet function but also potentially accelerating the onset of complications.

How to avoid these "traps"? The answer lies in staying away from processed foods and opting for natural, original ingredients
Ingredients. Cooking at home not only helps control sugar and fat intake but also promotes a healthier, more balanced diet. This "back-to-nature" eating style aligns with traditional Chinese medicine's health philosophy of "eating in moderation" and has gained widespread recognition in modern medicine.
Stress and Emotions: The "Invisible Driver" of Blood Sugar Fluctuations
Emotional fluctuations and stress are often overlooked hidden factors for diabetic patients. Modern medical research has found that when the human body is under stress, it secretes a large amount of stress hormones, such as cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones stimulate the liver to release more glucose into the bloodstream to cope with the "crisis."

However, for diabetic patients, this mechanism only worsens the situation, as their pancreatic islet function is already impaired and cannot effectively handle the additional blood sugar burden.

From a Traditional Chinese Medicine perspective, emotions are closely linked to internal organs. "Anger harms the liver, overthinking damages the spleen, and fear injures the kidneys" - emotional imbalances directly disrupt the equilibrium of organ functions, consequently affecting blood sugar stability. Particularly, anxiety and depression not only cause appetite disorders and poor sleep quality but also weaken immune function, making the body more susceptible to inflammatory attacks.

Managing emotions is a crucial part of diabetes management. Maintaining calm and learning stress reduction techniques not only helps stabilize blood sugar but also significantly improves overall health. Simple methods like deep breathing, meditation, and listening to music can effectively relieve stress. Traditional Chinese medicine also recommends acupuncture and massage to unblock meridians and alleviate emotional tension.
Ignoring Early Symptoms: A Breeding Ground for Complications
The most alarming aspect of diabetes lies in its complications. These complications often begin with seemingly "minor" symptoms, such as numbness in the hands and feet, blurred vision, or dry skin. However, many patients choose to ignore these "warning signals" simply because no significant discomfort is apparent, allowing the problems to progressively worsen until they eventually develop into severe diabetic foot, retinopathy, or kidney disease.

Traditional Chinese Medicine believes that "chronic illness inevitably leads to deficiency." Diabetic patients inherently suffer from qi and yin deficiency, making them more susceptible to external pathogens. These early symptoms are precisely the body's distress signals. If timely measures are taken to regulate and nourish the body, many complications can be prevented.
Modern medicine also advocates the principle of "early detection, early treatment," emphasizing the importance of regular screenings for diabetic patients. Whether it's fundus examinations, neurological tests, or urinary microalbumin detection, all are crucial tools for identifying complications.
The key to diabetes management is "prevention over cure." It's important to regularly observe changes in the body, promptly report them to your doctor, and adjust treatment plans periodically to keep risks under control at their earliest stages.
Alcohol Consumption and Blood Sugar Fluctuations: Hidden Dangers Between Drinks
Alcohol consumption is a frequently overlooked "trap" for many diabetic patients. Many believe that as long as they control their alcohol intake—such as drinking some red wine or beer—it won't affect their blood sugar levels.

However, this is not the case. Alcohol significantly impacts the liver's metabolic functions by inhibiting glucose release, thereby increasing the risk of hypoglycemia. Additionally, alcohol exacerbates insulin resistance, leading to more severe blood sugar fluctuations.

Traditional Chinese Medicine also regards alcohol as a "damp-heat substance," and excessive consumption can exacerbate internal damp-heat, worsening diabetes symptoms. Therefore, for individuals with diabetes, the best choice is complete abstinence from alcohol. If drinking is necessary, it should be strictly controlled under a doctor's guidance, opting for low-sugar and low-alcohol beverages.
Health management lies in the details
Diabetes management is not a one-time effort but a continuous process that permeates every aspect of life. From avoiding prolonged sitting to choosing healthy diets, from regulating emotions to paying attention to early symptoms, and practicing scientific alcohol cessation—these seemingly trivial details actually determine the quality of life and health future of diabetic patients.
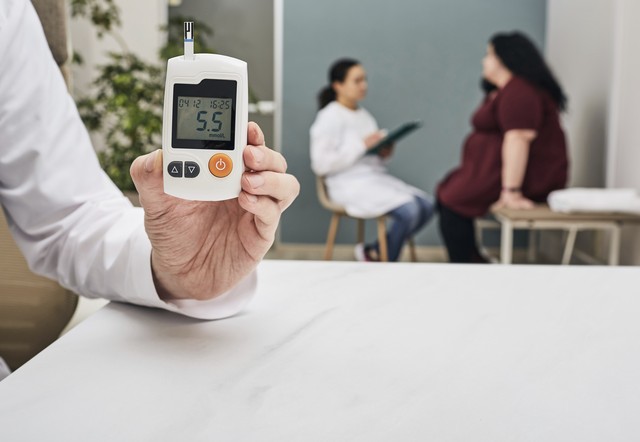

From a Traditional Chinese Medicine perspective, diabetes prevention and treatment focus on "regulation" – regulating diet, emotions, and daily routine. Western medicine, on the other hand, emphasizes scientific monitoring and standardized treatment. Only by combining both approaches can optimal results be achieved in diabetes management. For every diabetes patient, blood sugar management represents not just personal responsibility but also a commitment to their family.
May every diabetes patient start from the details and move towards a healthier life.