Want to understand Helicobacter pylori? First pinpoint where it is in the body
Key point: Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that inhabits the pyloric region of the human stomach. It matters because it can cause gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even increase the risk of stomach cancer, so knowing its location is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
Helicobacter pylori is a bacterium that inhabits the pyloric region of the human stomach. It matters because it can cause gastritis, peptic ulcers, and even increase the risk of stomach cancer, so knowing its location is crucial for diagnosis and treatment.
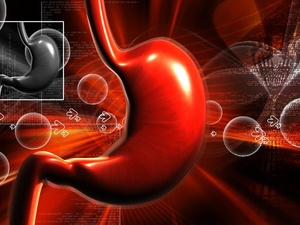
Helicobacter pylori primarily resides in the pyloric region of the stomach, which is the lower end of the stomach that connects to the duodenum. These bacteria damage the stomach’s protective mucous layer by producing toxins and other harmful substances, leading to inflammation and ulcers. They can also survive in the acidic environment of the stomach by adhering to the gastric mucosa and forming a protective layer to avoid being killed by stomach acid.
There are various methods to test for Helicobacter pylori, including breath tests, blood tests, stool tests, and gastroscopy. The numerical values in test results typically indicate the severity of infection; higher values often suggest a more serious infection. We should view these test results objectively, because a positive result does not necessarily mean serious health problems will occur. Treating H. pylori infection usually requires a combination of antibiotics and proton pump inhibitors, but during treatment one should be alert to possible side effects, such as antibiotic resistance and drug interactions.
【Practical tip:】
1. Pay attention to personal hygiene to prevent the spread of Helicobacter pylori.
2. If the test result is positive, follow medical advice and undergo standard treatment.
3. Avoid spicy and irritating foods in your diet to prevent worsening stomach discomfort.
4. Have regular follow-ups to monitor treatment effectiveness and stomach health.