How long does it take for reflux esophagitis to develop into esophageal cancer?
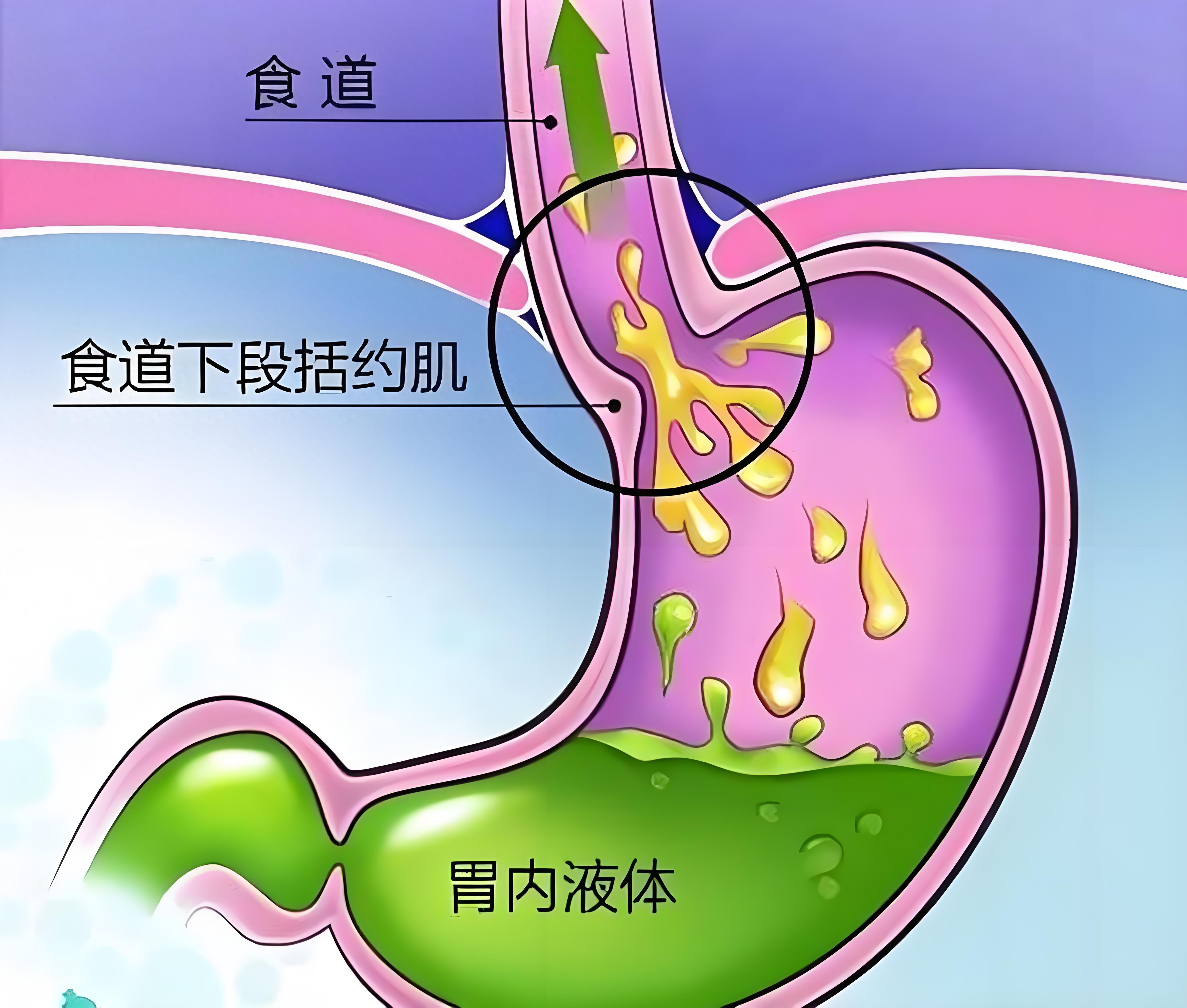
Reflux esophagitis is a common condition, with symptoms including chest pain, acid reflux, and belching. Long-term suffering from reflux esophagitis may increase the risk of developing esophageal cancer, but not all individuals with reflux esophagitis will develop esophageal cancer, and the time to progression to esophageal cancer varies from person to person.
According to research, approximately 1-5% of patients with reflux esophagitis eventually develop esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and the progression of this cancer typically takes many years.
In fact, esophageal cancer is typically caused by multiple factors, including age, genetics, environment, lifestyle, and diet. Therefore, reflux esophagitis is not the sole factor in developing esophageal cancer, but long-term reflux esophagitis may increase the risk of esophageal cancer.
If you suffer from reflux esophagitis, you should actively treat and control the condition to reduce the risk of developing esophageal cancer.
It is recommended to undergo treatment under the guidance of a physician and adopt a healthy lifestyle, such as following dietary advice and avoiding smoking and alcohol, to lower the risk of esophageal cancer.
Additionally, regular physical examinations and screenings can help detect and treat any potential esophageal cancer early, thereby improving the cure rate.