How should patients with liver disease who develop jaundice eat correctly?
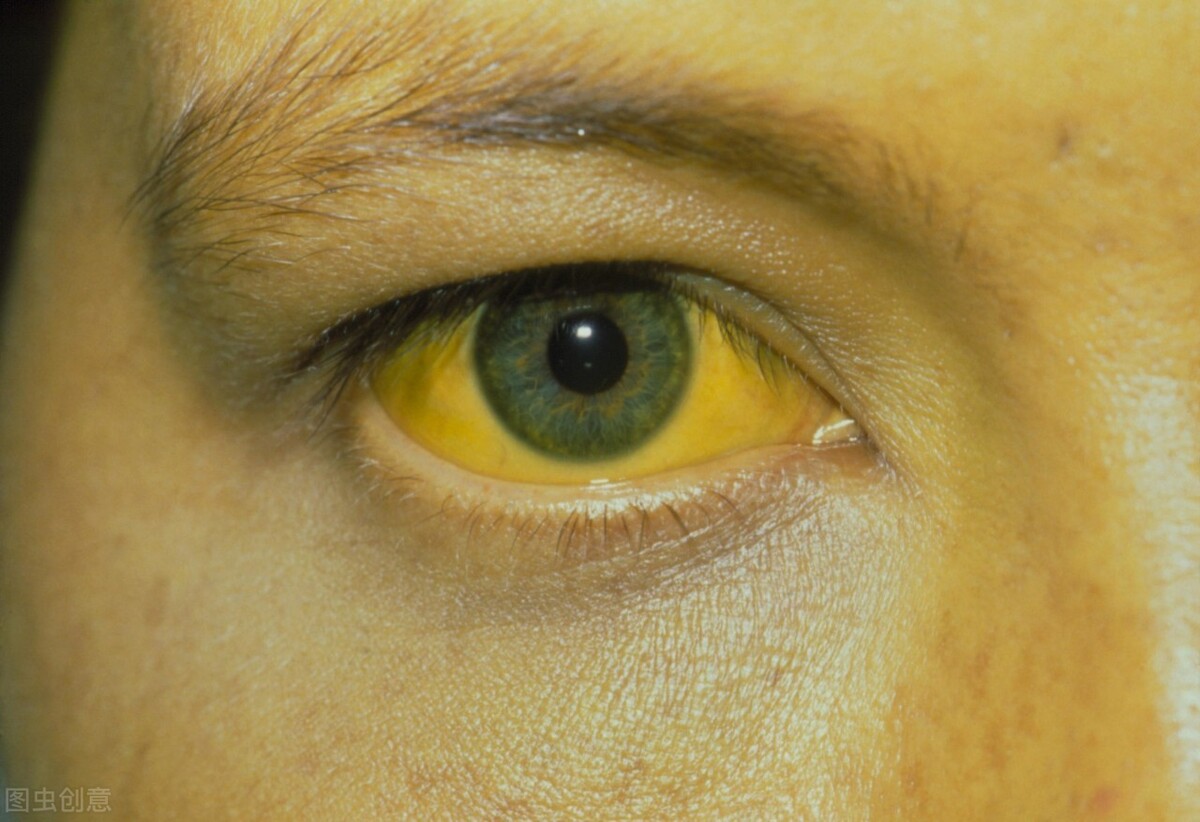
Jaundice is a common symptom frequently associated with liver disease, caused by a disorder in bilirubin metabolism leading to elevated bilirubin levels in the blood (hyperbilirubinemia). It is not a disease itself but typically manifests as yellowing of the sclera, skin, and mucous membranes. When jaundice occurs in liver disease patients, how should they properly adjust their diet?
I. Suitable diet for patients with jaundice
1. Water
Water is crucial for jaundice patients as it helps clear excess bilirubin and supports the liver and kidneys in detoxification. It is recommended that jaundice patients drink at least 3 liters of water daily. In addition to water, other fluids such as soup can also be consumed in appropriate amounts.
2. Fresh Fruits and Vegetables
Consuming fresh fruits and vegetables can greatly aid in recovery from the illness. They are rich in powerful antioxidants and fiber, easy to digest, and can also limit liver damage during metabolic processes. For example, citrus fruits contain electrolytes that help maintain the body's energy levels; papayas, berries, and melons are abundant in enzymes and trace elements, which can enhance cellular regeneration.
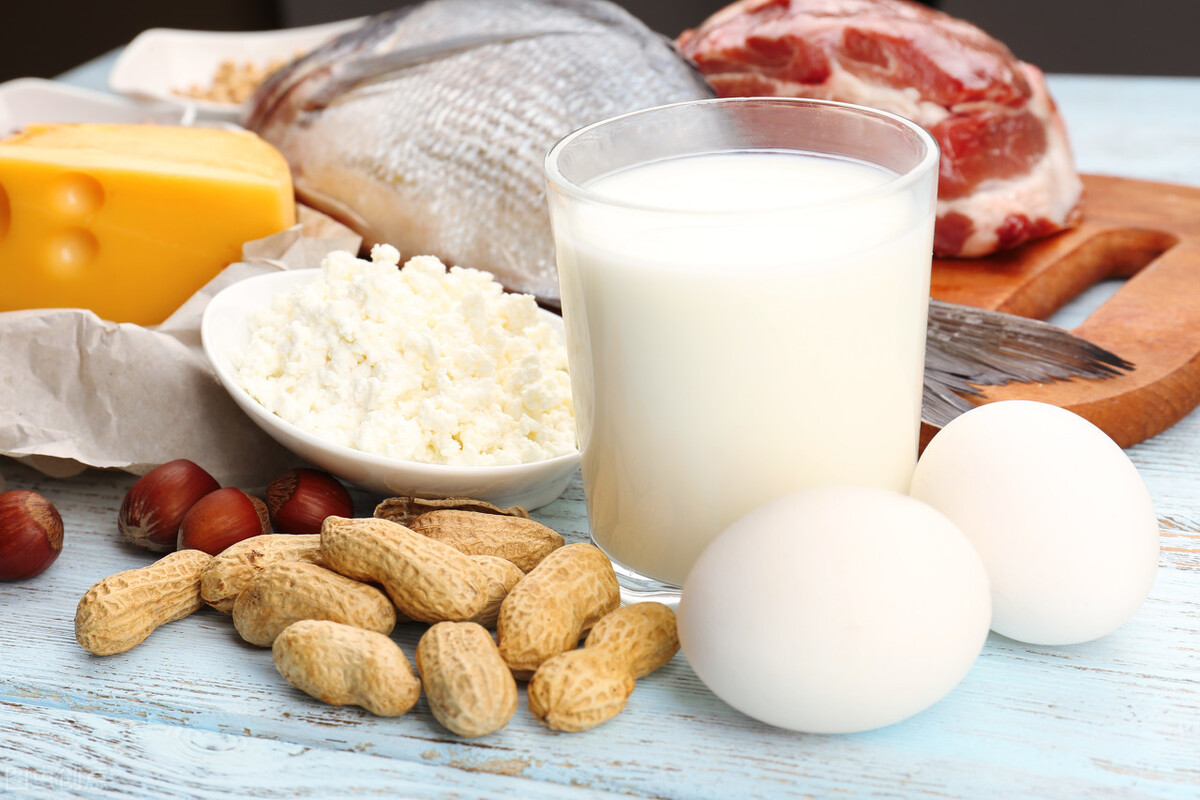
3. High-Protein Foods
When liver disease patients develop jaundice, appropriately increasing high-protein intake can help improve enzyme production, promote hormone synthesis in the body, and support the repair and regeneration of damaged cells. Options such as lean meat, eggs, and milk can be chosen.

4. Nuts and Legumes
Most nuts and legumes are rich in antioxidants, as well as fiber and healthy fats, and studies have shown that regular consumption of walnuts and other nuts helps improve liver function in patients with liver disease
5. High-fiber foods
Dietary fiber helps promote the movement of bile through the ducts, facilitates easier intestinal movement, helps control cholesterol levels, reduces stress on the liver, speeds up the elimination of toxins from the body, and supports liver recovery.
II. Foods that jaundice patients should avoid
1. Alcohol
Alcohol needs to be detoxified and metabolized by the liver. Its breakdown product, acetaldehyde, has a direct toxic effect on liver cells. Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to the development of chronic hepatitis, causing further fibrosis of the liver or even cirrhosis.
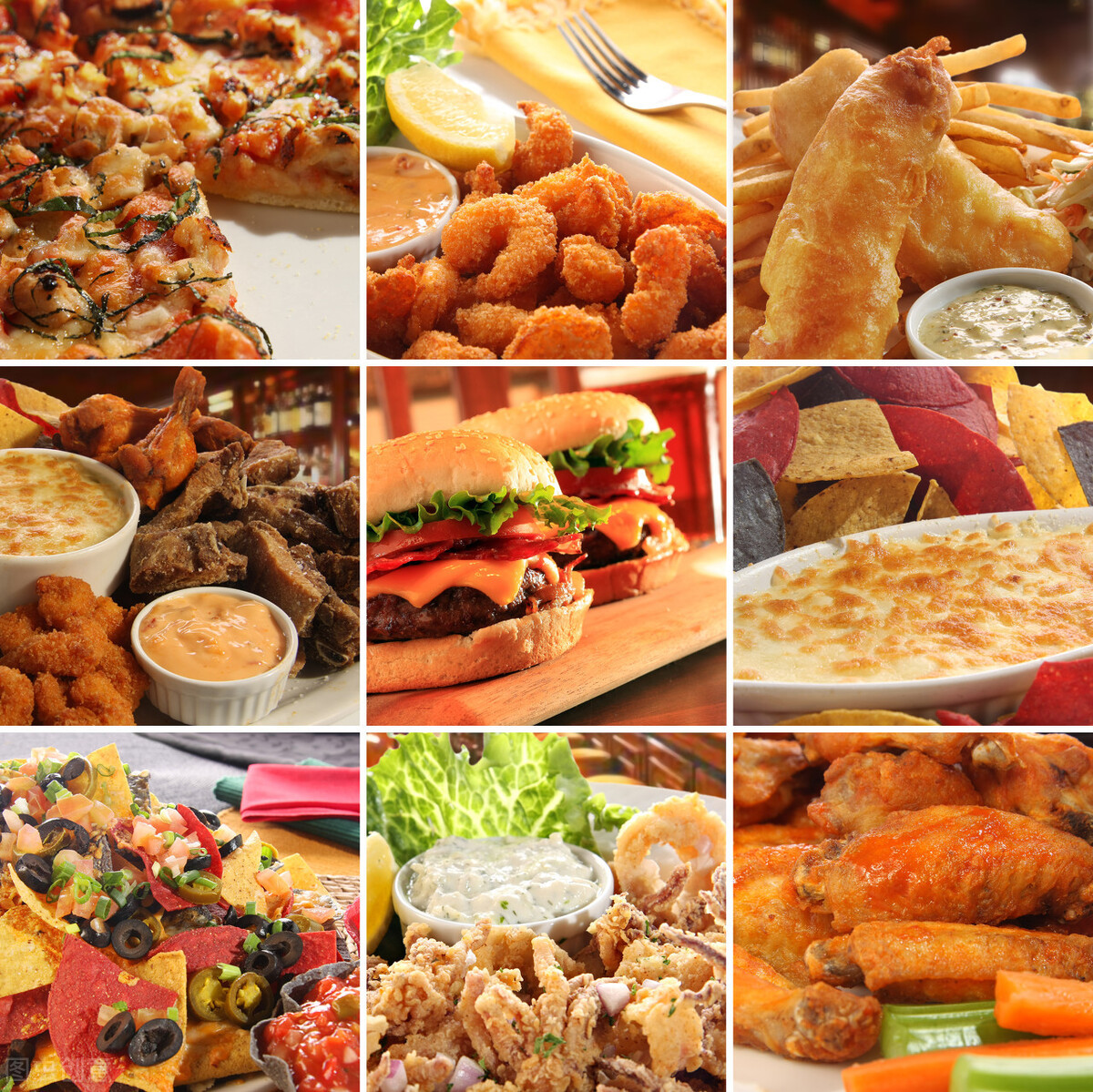
2. Saturated Fatty Acids and Trans Fatty Acids
Examples include fried foods, greasy foods, and fast food. Studies have shown that high intake of saturated and trans fatty acids is associated with obesity and malnutrition, both of which are risk factors for liver disease. Therefore, consumption of such foods should be avoided or limited as much as possible.

3. Processed and Smoked Foods
These foods contain large amounts of preservatives, such as nitrites and sulfates, which can lead to dehydration and increase the metabolic burden on the liver. It is advisable to limit the consumption of such foods.
Friendly Reminder: In addition to the dietary precautions mentioned above, patients with liver disease should maintain good daily routines, ensure adequate sleep, and avoid excessive fatigue. These practices are beneficial for recovery.