Confronting the Hepatitis B Five-Panel Test: A Guide to Correctly Analyzing Your Results!
Many people receive their physical examination reports only to be confused by the Hepatitis B five-panel test results. What does each item represent? What does it mean if several of them are positive? Today, we will directly address the Hepatitis B five-panel report and teach you how to correctly interpret the results!
I. What Does Each Item in the Hepatitis B Five-Panel Test Represent?
1. First Item: Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg)
It is the surface protein of the hepatitis B virus, and its presence is often associated with the existence of complete hepatitis B virus particles. Therefore, a positive result for this item is used as an indicator of hepatitis B virus infection, and if it persists for more than 6 months, the individual is considered a chronic hepatitis B virus carrier.
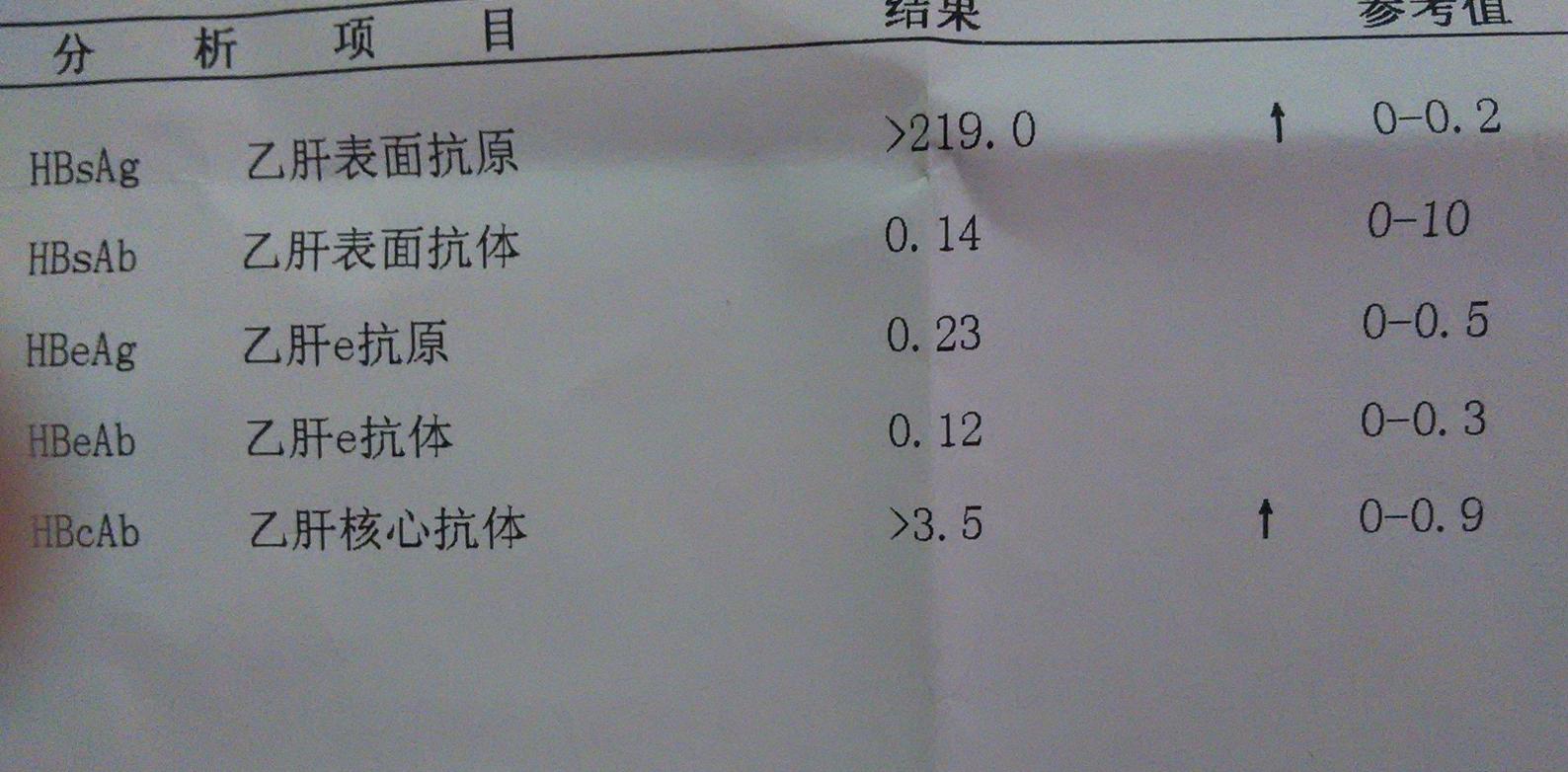
2. Second Item: Hepatitis B Surface Antibody (Anti-HBs)
It is an antibody produced by the body to fight against the hepatitis B virus. A positive result for this item indicates that the body has developed immunity to hepatitis B, either due to a past infection or as a result of receiving the hepatitis B vaccine.
3. Third Item: e Antigen (HBeAg)
Produced inside the virus and secreted into the bloodstream, it typically appears after hepatitis B virus infection as a marker of viral replication, indicating active hepatitis B virus and serving as an indicator of infectiousness.
4. Fourth Item: e Antibody (Anti-HBe, HBeAb)
Produced by the body in response to the e antigen. There are two reasons for a positive e antibody result: one is the disappearance of e antigen and the appearance of e antibody. In this case, the virus becomes less infectious, and the patient is in the recovery phase; the other is viral mutation, where the serum cannot produce e antigen, and further HBV-DNA testing is needed to determine the presence of hepatitis B virus.
5. Fifth Item: Core Antibody (Anti-HBc)
Indicates a past hepatitis B virus infection; this marker will be present regardless of whether the virus has been cleared or not.
II. How to Correctly Interpret the Hepatitis B Serology Panel Results
1. The first item is positive; the remaining four are negative.
Indicates the late stage of the incubation period of acute hepatitis B virus infection.
2. Positive for the first and third items, negative for the remaining three
Indicates the early stage of acute hepatitis B, with strong infectivity.
3. Positive for the first, third, and fifth items, negative for the remaining two
Commonly referred to as "HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B," this condition indicates acute or chronic hepatitis B, with active viral replication and high infectivity.
4. Positive for items 1 and 5, negative for the other two
Indicates acute or chronic hepatitis B.
5. Positive for items 1, 4, and 5, negative for the other two
Commonly known as the "small three yangs," it indicates acute or chronic hepatitis B, but with relatively weak infectivity.
6. The fifth marker is positive, while the other four markers are negative.
This indicates that the person is either a covert carrier of the hepatitis B virus or in the window period of infection, and it also suggests a previous infection with the hepatitis B virus.
7. Fourth and fifth items positive, the remaining three items negative
Indicates the recovery phase of hepatitis B, or past infection with the hepatitis B virus.
8. Second, fourth, and fifth items positive, the remaining two items negative
Indicates the recovery phase of hepatitis B, with immunity already established.
9. Second and fifth items positive, all other three items negative
Indicates either post-hepatitis B vaccination or recovery from hepatitis B virus infection, with existing immunity.
The "Hepatitis B Serology Panel" test only reflects HBV infection and replication status and does not fully indicate disease severity. To assess the severity of hepatitis B, in addition to the "Hepatitis B Serology Panel," it is necessary to combine results from liver function tests, liver fibrosis indicators, and imaging studies such as ultrasound and CT for an accurate evaluation of the current condition.