Factors Influencing the Survival Time of Patients with Ascites from Liver Disease: What You Need to Know!
As is widely known, hepatic ascites is a complication that occurs when conditions like liver cirrhosis or liver cancer progress to a certain stage. The presence of hepatic ascites indicates that the disease has reached a relatively severe level and may cause some physical discomfort.
Consequently, many patients begin to believe that they do not have much time left, worrying that their condition may threaten their lives. This often leads to feelings of pessimism, negativity, or even giving up on treatment. So, what factors influence the survival time of patients with hepatic ascites?
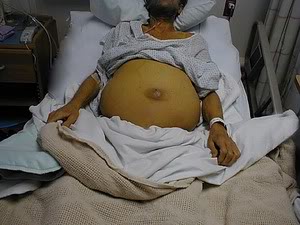
I. Factors Influencing the Survival Time of Patients with Ascites from Liver Disease
1. Condition
Although all patients with hepatic ascites share this symptom, each individual's situation is different, and their physical constitution varies as well. Therefore, a detailed and case-specific analysis is necessary.
Patients with poor physical condition and a negative attitude are prone to premature death, while optimistic patients with relatively better physical condition and milder illness tend to survive longer.
Therefore, regardless of the severity of the condition, it is crucial to build the courage and confidence to overcome the disease, which is very beneficial for treatment. Maintaining optimism and a positive outlook can greatly aid in recovery.
2. Treatment

Although many believe that hepatic ascites cannot be completely cured and treatment only serves to sustain life, it is precisely this "life-sustaining" treatment that affects the lifespan of patients with hepatic ascites.
A small number of patients experience relatively good outcomes during treatment, showing improvement in their condition. As long as patients with hepatic ascites have the correct attitude toward their disease and undergo scientific treatment, the condition can be effectively controlled, and their lifespan can naturally be extended.
To achieve effective treatment, early detection and timely intervention are key. So, how can one detect hepatic ascites as early as possible?
II. Early Symptoms of Ascites from Liver Disease
1. Abdominal distension
A large amount of ascites can lead to abdominal distension and tightness of the abdominal wall. Patients may experience difficulty walking, shortness of breath, and umbilical hernia in their daily lives.
2. Abdominal Distension
Most patients do not exhibit any symptoms in the early stages; some patients may occasionally feel abdominal distension.

3. Abdominal Pain
As the condition progresses, symptoms of abdominal pain may also occur. Patients often overlook this abdominal pain and do not associate it with hepatic ascites.
4. Edema
Edema is a symptom that can appear in the early stages of liver ascites. If edema persists for a long time, it should be taken seriously, and medical attention should be sought promptly.
Reminder: Because the early symptoms of liver ascites are not obvious, patients with cirrhosis should pay special attention to any discomfort they experience. Once symptoms such as those described above appear, it is necessary to undergo examination at a hospital as soon as possible to confirm the diagnosis. If liver ascites complications are confirmed, timely measures should be taken for targeted treatment to avoid missing the optimal early treatment period for liver ascites and to prevent potential threats to health and life.