How Serious is Fatty Liver Disease Found in a Physical Exam? Is It Okay Not to Treat It?
With the improvement in living standards, fatty liver disease has gradually become a threat to people's health, and the trend of younger onset ages should not be underestimated.
Many people believe that fatty liver disease is caused by obesity and that controlling weight is all that matters. But is that really the case? I would like to tell everyone that severe fatty liver disease, if left unchecked, can also progress to liver cirrhosis. So, first of all, everyone needs to understand: What is fatty liver disease?
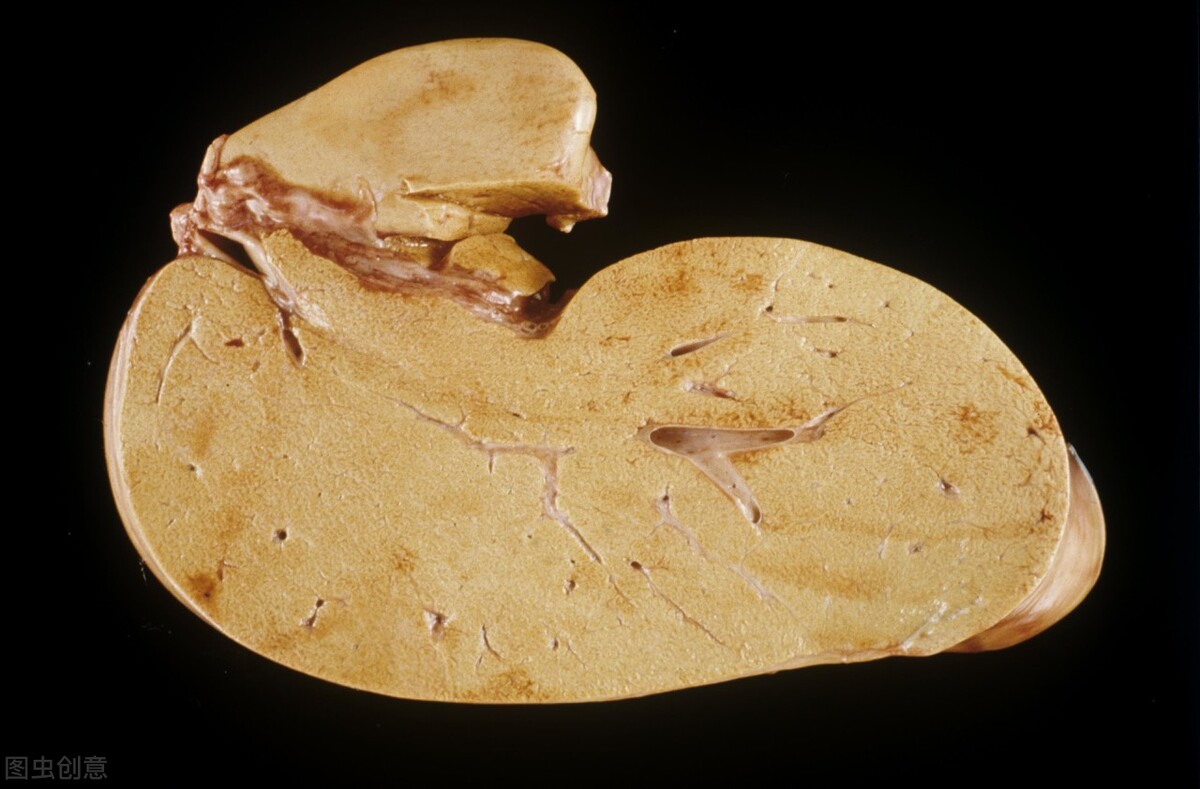
Fatty liver disease refers to pathological changes characterized by excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells due to various reasons. It is a common pathological alteration of the liver and not a specific or independent disease.
Fatty liver disease is a reversible condition. Mild fatty liver generally does not require medical treatment, and paying attention to the following four aspects in daily life is sufficient.
1. Maintain a Reasonable Diet
A significant portion of fatty liver cases is attributed to improper diet. Therefore, in daily life, it is essential to adhere to a standardized eating pattern. As the saying goes: "Eat a hearty breakfast, a filling lunch, and a light dinner."
In daily life, it is important to drink plenty of water, consume fresh fruits and vegetables, and moderately incorporate high-fiber and high-protein foods, such as whole grains, meat, dairy, eggs, fish, shrimp, legumes, and nuts. Avoid fried foods, spicy and irritating foods, ensure three meals a day, refrain from late-night snacks, and reduce the consumption of snacks and carbonated beverages.
2. Control Alcohol Intake
Patients with fatty liver should limit or avoid alcohol consumption, as alcohol is a significant factor contributing to fatty liver disease, slowing liver metabolism and impairing liver function.

3. Increase Exercise and Reduce Weight
Engaging in regular and appropriate exercise can strengthen the body and enhance immunity, while effective aerobic exercise improves microcirculation. For obese patients, incorporating fat-reducing exercises and maintaining physical activity can help alleviate liver steatosis.
4. Blood Sugar Control
According to statistics, the incidence of fatty liver combined with diabetes is as high as 41%. For diabetic fatty liver, it is crucial to strictly control blood sugar levels, as well-managed blood sugar can promote the reduction of fat in the liver. Therefore, maintaining blood sugar within an ideal range is key to treating fatty liver.
So, when is treatment necessary for moderate to severe fatty liver?
First, fatty liver hepatitis requires treatment, which means when imaging reveals fatty liver and liver enzymes are abnormal—specifically, alanine transaminase or alkaline phosphatase being one to five times above normal levels—and this condition persists for more than four weeks, medication is absolutely necessary. Of course, this should be combined with dietary and exercise interventions;
The second scenario is when liver enzyme levels are normal, but a biopsy reveals manifestations of fatty liver hepatitis, showing inflammatory changes. In such cases, medication intervention is also required.
Director Sun kindly reminds you: Although fatty liver disease is a reversible condition, everyone should still take it seriously. If not intervened in a timely manner and left to progress, it can develop into fibrosis, cirrhosis, or even liver cancer. This is not to scare you—fatty liver disease has now become the second leading risk factor for liver cancer, so it's crucial not to ignore it!